Fourth, rigid flexible printed board production process:
1. Rigid-flex PCB materials: Rigid-flex PCBs use flexible materials in addition to rigid materials such as epoxy glass cloth laminates and prepregs or polyimide laminates and corresponding prepregs.
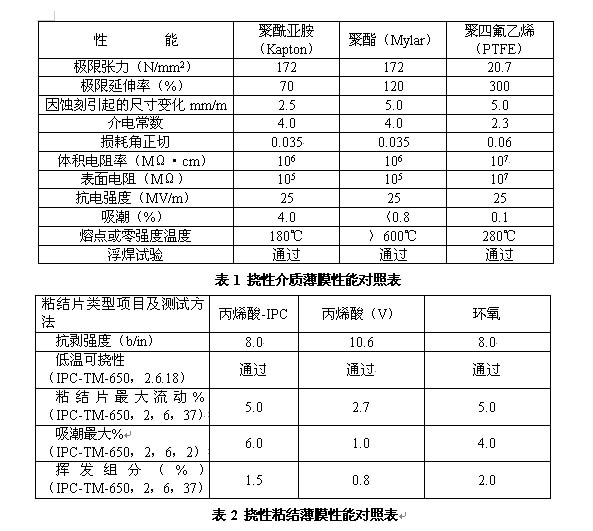
Flexible materials: Commonly used flexible media films include polyesters, polyimides, and polyfluorines. Selecting flexible media should be based on a comprehensive investigation of the material's heat resistance, formability, and thickness; commonly used adhesives There are mainly acrylic films, epoxy resins and polyester films. Selecting adhesive films mainly examines the fluidity of the materials and their coefficient of thermal expansion (Table 1 and Table 2 show the properties of flexible films).
Copper foil: Copper foil used in printed boards is mainly classified into electrolytic copper foil (ED) and rolled copper foil (RA). The electrolytic copper foil is formed by electroplating, and the crystal state of the copper particles is vertical needle-like, easy to form a vertical line edge during etching, which is favorable for the production of fine lines; but when the bending radius is less than 5mm or dynamic deflection, needle-like The structure is easy to break; therefore, the flexible copper-clad substrate is mostly made of rolled copper foil. The copper particles have a horizontal axis structure and can adapt to multiple deflections.
2. Flexible inner imaging and etching:
Pre-treatment:
The copper foil on the surface of the copper clad laminate is protected from oxidation. The surface of the copper foil has a dense oxide protective film. Therefore, the surface of the flexible copper clad laminate must be cleaned and roughened before imaging. However, since the flexible sheet is liable to be deformed and bent, a special pumice machine or micro-etching may be used. For the general manufacturer, microetching is recommended to reduce the extra equipment investment.
In the process of microetching, the degree of roughening on the surface of the board and the uniformity of the roughening should be controlled. It is recommended that the microetching solution be a sodium persulfate (Na2S2O4) and sulfuric acid (H2SO4) type microetching solution to prevent excessive roughening of the board surface. Or part of the board surface roughening is insufficient; at the same time, in order to prevent the card board or sheet material from falling into the microetching liquid during the microetching process, a rigid board may be stuck before the flexible board (development and etching should also be adopted).
Pay attention to the holding of the plate to be very careful, because the dents or creases of the plate will cause the bottom plate can not be tight and cause the pattern to shift when the exposure.
Imaging and etching:
Dry film imaging is recommended to reduce plate rework (when wet film imaging is used, wet film pre-baking is difficult and the rework rate is high). Pay attention to the holding of the plate to prevent folding, development, and rigid plate traction during development and etching.
Note: The imaging and etching of the rigid inner layer is basically the same as the imaging and etching of the inner layer of the rigid rigid multilayer board. It is not introduced here.
Open window of rigid outer layer and rigid prepreg:
Window opening can be done by using a twister. To prevent the flow of glue at the opening of the window when rigid-flexing the printed board, the window of the rigid prepreg should be slightly larger than the window of the rigid outer layer (usually 0.2-0.4 larger than the window of the rigid outer layer). Mm is preferred, and the thicker the rigid prepreg, the more rigid the window of the rigid prepreg should be than the window of the rigid outer layer. When opening the window, note that the rigid outer layer or rigid prepreg is nailed and secured with wrinkle glue so that the edge of the opened window is not neat or the size does not match the design.
Lamination of flexible layers and rigid-flexible multilayer printed boards:
The etched rigid-flex PCB flexible laminates have to be treated with a surface to increase the bonding force before the rigid outer layer is pressed. The surface treatment can be microetched or pumice milled; the flexibility after surface treatment is Moderate drying should be performed before lamination to remove moisture from the flexible inner layer.